The Unseen Risk.
The electronic exchange of personal information has grown exponentially as the use of technology expands in all fields including healthcare, banking, social media and gaming. The information that companies collect on individuals, how it is stored, transferred or used is source of concern for many and rightfully so. A quick look at data breaches in the last decade show just how vulnerable personal information can be. The major breaches include:
• Yahoo (2013-14): 3 billion user accounts
• Sina Weibo (2020): 538 million user accounts
• Marriott International (2014-18): 500 million customers
• Zynga (2019): 218 million user accounts
• Adobe (2013): 153 million user records
Cyber-attacks and data breaches in the healthcare sector is particularly troubling given the sensitive nature of the information. Notable data breaches in healthcare include the 2015 attack on Anthem where nearly 80 million consumers were impacted and the 2019 attack on American Medical Collection Agency that exposed personal of 24 million people.
In light of this constant threat to personal information, in May 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into effect. GDPR regulates how a company can collect, store, and use data on citizens of European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA).
Under GDPR individuals have the following basic rights:
• Access to personal data
• Data deletion upon request
• Data portability
• Informed consent prior to data gathering
• Data corrected and updated
• Restrict how a company uses their data
• Data breach notification within 72 hours
The EU is taking this very seriously. There are two tiers of administrative fines that can be levied as penalties for non-compliance:
1. Up to €10 million or 2% of annual global total revenues
2. Up to €20 million or 4% of annual global total revenues
In 2019 British Airways felt the sting of non-compliance as it was levied a £183 million fine. The Information Commissioner’s Office announced that it was the largest penalty ever imposed. The previous record was held by Facebook for its part in the Cambridge Analytica scandal (£500,000). In the end, BA got out lightly since it avoided the maximum penalty of 4% of total revenue which would have meant a fine closer to £183 million.
GDPR has now been in effect for more than two years but in a survey of 600 US, UK and other EU companies, TrustArc, a privacy compliance company, reports that only 20% of the companies have fully completed their GDPR implementations. 27% of companies have not started the work towards GDPR compliance. In the US, leaders need to be aware that these regulations apply to their organizations if they handle the data of EU and EEA citizens. GDPR compliance requires a company-wide commitment to the management of private data which may include implementing new policies and procedures and regular employee training.
Creating Value Through Compliance
At Cadence, the work we do is in market research and medical communications for healthcare companies. We regularly speak with physicians, academics, nurses, and patients across a wide variety of disease states. In order to become GDPR compliant as a company we have improved these four key aspects of data privacy and security: physical security, digital security, transferring personal data and individual employee responsibility.
Cadence has taken GDPR very seriously and is continually making process and policy improvements to keep up with multiple, complex compliance requirements. Most recently we received International Privacy Verification from TrustArc. It has taken just over a year and a significant financial commitment to complete this process. We did this in order to protect the data of the individuals we work with and to better service our global client-base. We also believe that we are providing value to our clients even if it isn’t a visible form of service. One bottom line benefit for us is that we have competitive advantage working with clients who need vendors that are GDPR compliant.
Some of the measures that we have communicated and encouraged in our staff is shown below:
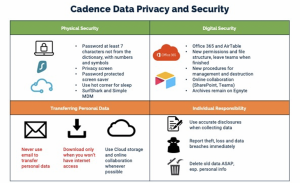
Compliance with GDPR translates to direct benefit for our clients in terms of protecting them from GDPR violations. An example would be a client sponsored medical advisory board involving European physicians. The information that is collected on each participant is personal. Mishandling that information can result in fines directed at the client, the vendor and the sponsor.
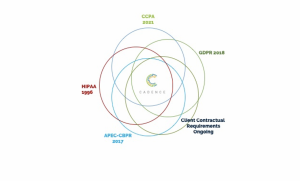
Cadence is well versed in data privacy and security regulations, complying with numerous laws including HIPAA, CCPA, APEC-CBPR, GDPR, as well as client specific requirements.
To learn know more about GDPR or Cadence, reach out to me directly at sbiswas@cadenceresearch.com.





